Linked Lists
A linked list is a data structure that stores items in sequence. Each node contains a value and a reference to the next node in the list. The first node is the head and the last node is the tail. The tail's next field is null.
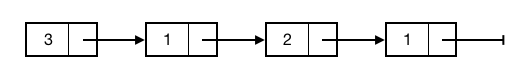
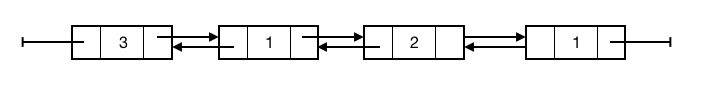
Nodes in doubly linked lists also contain a reference to the predecessor.
Linked Lists vs. Arrays
A list is similar to an array in that it contains objects in linear order. The key differences are that inserting and deleting elements in a list has time complexity \(O(1)\). On the other hand, obtaining the kth element in a list is expensive, having \(O(n)\) time complexity.
Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self, value, next=None):
self.value = value
self.next = next
Search
def search(key, linked_list):
"""Find the Node with value=key. Return None if not found."""
while linked_list and linked_list.key != key:
linked_list = linked_list.next
return linked_list
Reverse
def reverse(head):
"""Reverse a singly linked list."""
to_return = None
while head:
buffer = head
head = head.next
buffer.next = to_return
to_return = buffer
return to_return
Find Cycle
def has_cycle(head):
"""Use Floyd's Tortoise and Hare algorithm to check for a cycle."""
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast is slow:
return True
return False